The rapid rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has fueled the demand for wireless technologies that can connect billions of devices efficiently. Traditional connectivity solutions like Wi-Fi and cellular networks offer high bandwidth, but they are often power-hungry and limited in coverage. This gap has been filled by Low-Power, Wide-Area Networks (LPWANs), with LoRaWAN® emerging as one of the most widely adopted standards for long-range, low-power IoT communications.
LoRaWAN® is a leading LPWAN technology that enables long-range, low-power communication for massive IoT deployments. Its flexibility, open standardization, and proven use cases make it an ideal choice for industries looking to harness IoT for smarter, more sustainable operations.
LoRaWAN® (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a low-power, wide-area networking protocol designed for IoT devices that require secure, long-range communication with minimal energy consumption. It operates on top of the LoRa® (Long Range) physical layer, a spread-spectrum modulation technique derived from chirp spread spectrum (CSS) technology.
- LoRa® handles the physical radio communication between devices and gateways.
- LoRaWAN® defines the network architecture, device classes, message structure, and security mechanisms that enable interoperability and scalable deployments.
This combination allows devices to send small amounts of data over several kilometers while running for years on a single battery.
Key Features of LoRaWAN®
- Long Range Coverage
- Urban coverage: up to 2–5 km.
- Rural coverage: up to 15–20 km or more (depending on terrain and gateway placement).
- Low Power Consumption
- End devices are optimized for energy efficiency.
- Typical battery life: 5–10 years, depending on transmission frequency and payload size.
- Scalability
- A single LoRaWAN® gateway can handle thousands of end devices.
- Suitable for massive IoT deployments in smart cities and industries.
- Security
- End-to-end encryption using AES-128 at the network and application layers.
- Ensures confidentiality, authenticity, and integrity of transmitted data.
- Flexibility in Deployment
- Supports both public (operated by telecom providers) and private networks.
- Enterprises can build and operate their own LoRaWAN® infrastructure.
1. LoRa Alliance®
- Role: Non-profit association managing the LoRaWAN® standard.
- Capabilities:
- Defines and maintains the LoRaWAN® protocol specification.
- Ensures interoperability through certification programs.
- Grows the ecosystem with over 500 member companies (operators, device makers, solution providers).
2. Semtech Corporation
- Role: Original developer of LoRa® modulation technology.
- Capabilities:
- Supplies LoRa® chipsets (transceivers, gateways).
- Provides reference designs for IoT modules.
- Partner ecosystem enabling satellite LoRaWAN® and edge solutions.
3. Kerlink
- Role: LoRaWAN® network infrastructure provider.
- Capabilities:
- Offers indoor/outdoor gateways and network servers.
- Provides WAN management platforms for large-scale IoT deployments.
- Expertise in smart agriculture, utilities, and logistics.
4. The Things Industries (TTI) / The Things Network (TTN)
- Role: Global LoRaWAN® open-source and enterprise ecosystem.
- Capabilities:
- Runs The Things Stack, a cloud-native LoRaWAN® network server.
- Provides community-based networks (TTN) and enterprise-grade solutions (TTI).
- Developer-friendly tools, APIs, and integration with AWS, Azure, Google Cloud.
5. Actility
- Role: Industrial LoRaWAN® network provider.
- Capabilities:
- Offers ThingPark™ platform for carrier-grade LoRaWAN® deployments.
- Supports geolocation, roaming, and multi-tenant management.
- Partnerships with telecom operators to enable nationwide LoRaWAN® coverage.
6. Senet
- Role: LoRaWAN® public network operator (U.S.).
- Capabilities:
- Provides LoRaWAN® as a Service (LaaS).
- Operates one of the largest carrier-grade public LoRaWAN® networks in North America.
- Offers smart metering, smart city, and logistics solutions.
7. MachineQ (by Comcast)
- Role: Enterprise LoRaWAN® platform provider.
- Capabilities:
- Delivers enterprise-grade gateways and cloud-based network management.
- Focus on retail, healthcare, facilities, and asset tracking.
- Scalable deployments backed by Comcast’s infrastructure.
8. MultiTech
- Role: Hardware manufacturer for LoRaWAN®.
- Capabilities:
- Produces LoRaWAN® gateways, modems, and sensor modules.
- Offers developer-friendly kits for prototyping.
- Integrates with cloud platforms and private LoRaWAN® deployments.
9. OrbiWise
- Role: LoRaWAN® network software provider.
- Capabilities:
- Provides OrbiWAN™ Network Server for operators and enterprises.
- Supports large-scale carrier deployments.
- Expertise in smart utilities, agriculture, and logistics.
10. ChirpStack (Open Source Project)
- Role: Community-driven LoRaWAN® network server software.
- Capabilities:
- Open-source LoRaWAN® network server stack for private deployments.
- Supports multi-tenancy, integrations, and flexible deployments.
- Used by developers, enterprises, and research institutions.
11. Telecom Operators (Nationwide LoRaWAN® Coverage Providers)
- Examples: Orange (France), Proximus (Belgium), Swisscom (Switzerland), KPN (Netherlands).
- Capabilities:
- Offer public LoRaWAN® networks covering entire countries.
- Enable IoT roaming and cross-border coverage.
- Serve smart city, energy, and national-scale deployments.
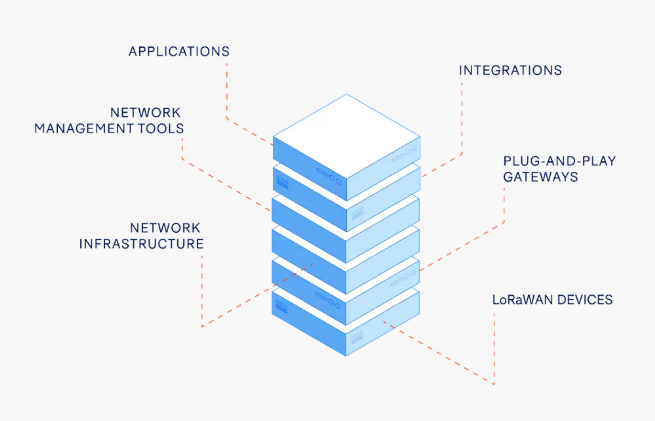
LoRaWAN® Network Architecture
A LoRaWAN® network follows a star-of-stars topology, consisting of:
- End Devices (Nodes): Sensors, trackers, meters, or actuators that send data.
- Gateways: Relay messages between end devices and the network server via IP backhaul (Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or cellular).
- Network Server: Manages device authentication, message routing, and deduplication.
- Application Server: Processes the collected data for analytics and business applications.
This architecture is highly efficient, enabling bi-directional communication (uplink and downlink), multicast support, and device management.
Device Classes in LoRaWAN®
LoRaWAN® defines three device classes to balance latency vs. power consumption:
- Class A:
- Default mode for all devices.
- Devices transmit uplink messages and open two short downlink windows afterward.
- Lowest power consumption, suitable for battery-powered sensors.
- Class B:
- Adds scheduled downlink windows synchronized via beacons from the gateway.
- Useful for devices needing periodic updates.
- Class C:
- Nearly continuous downlink windows, with the highest power consumption.
- Best for mains-powered actuators or control systems.
Advantages of LoRaWAN®
- Wide coverage at low cost (unlicensed ISM bands: 868 MHz in Europe, 915 MHz in North America, 433 MHz in Asia).
- High device density—thousands of nodes per gateway.
- Supports mobility and geolocation without GPS, using signal triangulation.
- Open ecosystem with interoperability through the LoRa Alliance® standardization.
Applications of LoRaWAN®
LoRaWAN® powers a broad range of IoT use cases across industries:
- Smart Cities
- Parking management, street lighting control, waste bin monitoring, and air quality sensors.
- Smart Agriculture
- Soil moisture sensors, livestock tracking, irrigation system monitoring.
- Utilities & Energy
- Smart water, gas, and electricity metering.
- Grid monitoring and leak detection.
- Industrial IoT
- Asset tracking, predictive maintenance, and supply chain visibility.
- Environmental Monitoring
- Flood detection, forest fire monitoring, climate data collection.
- Healthcare & Logistics
- Patient monitoring, vaccine cold chain tracking, and shipment monitoring.
Challenges and Limitations
- Data rate and bandwidth limitations: LoRaWAN® supports small payloads (typically 51–222 bytes per message). Not suitable for video or large data transfers.
- Duty cycle restrictions: Regulations limit how often devices can transmit, especially in the EU.
- Interference risks: Operating in unlicensed spectrum can lead to congestion in high-density areas.
- Security risks if misconfigured: Proper key management is critical.
The Future of LoRaWAN®
LoRaWAN® continues to evolve, with support for satellite-based LoRaWAN® networks, firmware updates over-the-air (FUOTA), and integration with edge AI for local decision-making. The LoRa Alliance®, a global association of more than 500 companies, is driving the growth and standardization of the technology.
With its balance of range, cost, energy efficiency, and scalability, LoRaWAN® is expected to remain a cornerstone of global IoT infrastructure, particularly in applications where long battery life and remote connectivity are essential.
MachineQ, a Comcast Company, announced the latest release of its low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) platform designed to reduce the complexities for businesses to develop and deploy Internet of Things (IoT) solutions at scale.
Based on the LoRaWAN® protocol, the MachineQ connectivity platform fully integrates gateway hardware with centralized network management tools for companies needing a more cost-effective, streamlined approach to building LPWAN solutions. Initially released in 2019, the MachineQ platform now processes millions of transmissions daily, and supports a growing base of both enterprise customers and LoRaWAN solution providers across the United States and Canada.
According to a recent Voice of the Enterprise study from 451 Research, part of S&P Global Market Intelligence, companies looking to deploy IoT face significant challenges today, including the ability to take IoT projects from proof of concept (POC) out to scale. 70% of enterprises reported problems with IoT projects getting beyond the POC stage, with one-third calling it a major problem1. Another challenge is a lack of employees with specialized IoT skills. The report notes that as a result of these challenges, enterprises are increasingly turning to other organizations – from outsourcers to cloud providers – to help with their IoT initiatives.
“The new version of our platform is tailored to meet the needs of enterprises to scale IoT, and is already being used by some of the world’s best-known companies. We’ve had great success leveraging nationwide IT deployment services from Comcast Business for our IoT projects,” said Steve Salata, general manager of MachineQ. “Our all-in-one offering gives organizations the benefit of working with a single connectivity partner and avoiding the complexity that is common when working with multiple providers.”
MachineQ’s fully integrated IoT connectivity platform makes it easy for operational and information technology professionals to set up and manage LoRaWAN networks and solutions. And, its monitoring and analytics tools can track and analyze IoT data in real-time to provide important insights to help solve a range of business challenges. The company works with both enterprises and a growing ecosystem of channel partners who harness the MachineQ platform for use cases such as food service safety and compliance, asset tracking, building and facilities management, and smart cities.
MachineQ is an active member of the LoRa Alliance®, a non-profit association committed to enabling large-scale deployment of LPWAN for IoT through developing and promoting the LoRaWAN open standard. The company is a gold-level sponsor for the Alliance’s Destination LoRaWAN webcast series, and recently participated in a webcast titled “Best Practices in Scaling LoRaWAN Solutions.” Executives from Microsoft and CoreKinect® joined MachineQ as panelists for the virtual event. Watch the replay here.
IoT Connectivity & Solutions – MachineQ, a Comcast Company
| Organization | Core Capabilities |
|---|---|
| LoRa Alliance® | Standards, interoperability, ecosystem growth |
| Semtech | LoRa® chipsets, hardware IP, ecosystem enablement |
| Kerlink | Gateways, network infrastructure, smart industry solutions |
| TTI / TTN | Network server software, developer ecosystem, cloud integrations |
| Actility | Carrier-grade platforms, IoT roaming, operator partnerships |
| Senet | Public LoRaWAN® network in U.S., LaaS model |
| MachineQ | Enterprise IoT networks, retail/healthcare solutions |
| MultiTech | Gateways, modules, developer kits |
| OrbiWise | Network server (OrbiWAN™), enterprise solutions |
| ChirpStack | Open-source network server, customizable deployments |
| Orange / Proximus / Swisscom / KPN | Nationwide LoRaWAN® connectivity for smart cities & utilities |
