Joby Aviation is an aerospace company, developing electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft that it intends to operate as an air taxi service. Electric aircraft, that is faster, cleaner, and a smarter way to have aerial ride.
Powered by six electric motors, our aircraft takes off and lands vertically, giving us the flexibility to serve almost any community.

With more than 1,000 test flights completed over the last 10 years, our aircraft has been designed to meet the uncompromising safety standards set by the FAA and other global aviation regulators. Joby aviation team is now engaged in a multi-year testing program with the FAA to certify our vehicle for commercial operations.
It has achieved an important milestone in the development of its aircraft, flying a full-size prototype vehicle more than 150 miles on a single charge, including a vertical take-off and landing.

The flight was completed at Joby’s Electric Flight Base in Big Sur, CA as part of the company’s ongoing flight test campaign.
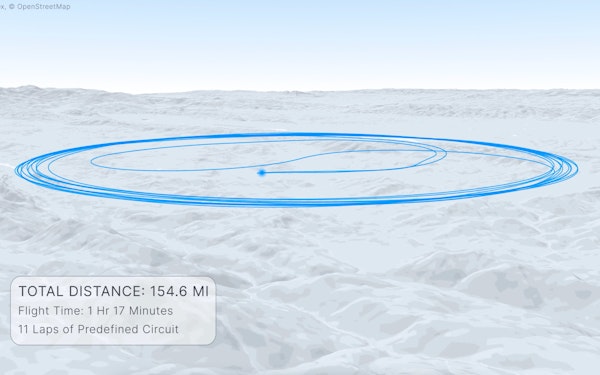
The aircraft, piloted from the ground by Joby’s Chief Test Pilot, Justin Paines, took off vertically before transitioning to forward flight and completing 11 laps of a predefined circuit. After more than 1 hour and 17 minutes in the air, the aircraft landed vertically, having covered a total distance of 154.6 statute miles.
Joby’s prototype aircraft uses commercially available lithium ion batteries that have been adapted for aerospace use. An 811 NMC cathode and a graphite anode cell were selected, following internal testing, to deliver the optimal trade-off between the specific energy required to fly the aircraft 150 miles, the specific power to take-off and land vertically and the cycle life to deliver an affordable service. We have demonstrated in the lab that this battery is capable of more than 10,000 of our expected nominal flight cycles.
Joby’s aircraft is expected to start commercial passenger service in 2024, transporting a pilot and four passengers at speeds of up to 200 mph.
The company is working towards certifying its aircraft with the Federal Aviation Administration, having already agreed on a “G-1” certification basis and been awarded a US Air Force Airworthiness Approval.
