DeepSource: A Comprehensive DevSecOps Platform for Code Health and Security
In modern software development, shipping code rapidly must not come at the expense of quality or security. Static code analysis, once a niche tooling area, has become an expectation for engineering teams aiming to minimize bugs, reduce technical debt, and catch vulnerabilities early in the development lifecycle.
DeepSource is a unified DevSecOps platform built to automate these objectives — combining static analysis, security scanning, code quality checks, dependency risk management, and automated fixes into a single workflow-native solution.
What Is DeepSource?
DeepSource is a cloud-native code health and DevSecOps platform that:
- Automatically analyzes source code and dependencies for quality issues and security vulnerabilities
- Integrates tightly into modern Git-based workflows
- Runs analysis on every commit and pull request
- Provides automated remediation suggestions via AI-powered tools
- Aggregates insights into dashboards and custom reports
It is designed to help teams shift quality and security left — catching issues before they reach the main branch or production.
Trusted by thousands of teams — from startups to enterprises — DeepSource positions itself as the modern alternative to older, heavier tools like SonarQube and traditional static-analysis products.
Core Capabilities
1. Static Code Analysis
At its core, DeepSource runs static analysis on source code — meaning it inspects code without executing it to find:
- Bugs
- Code smells
- Anti-patterns
- Performance issues
- Style inconsistencies
These analyzers work across many popular languages, including Python, JavaScript, Go, Java, Rust, Ruby, C#, PHP, and more, with coverage expanding over time.
Key Properties
- Thousands of built-in checks
- Fast analysis runs on pull requests
- Detects issues at the exact line of code
- Minimizes noise and false positives
This level of analysis helps developers detect objective problems early — such as missing null checks or potential performance regressions — before they propagate further.
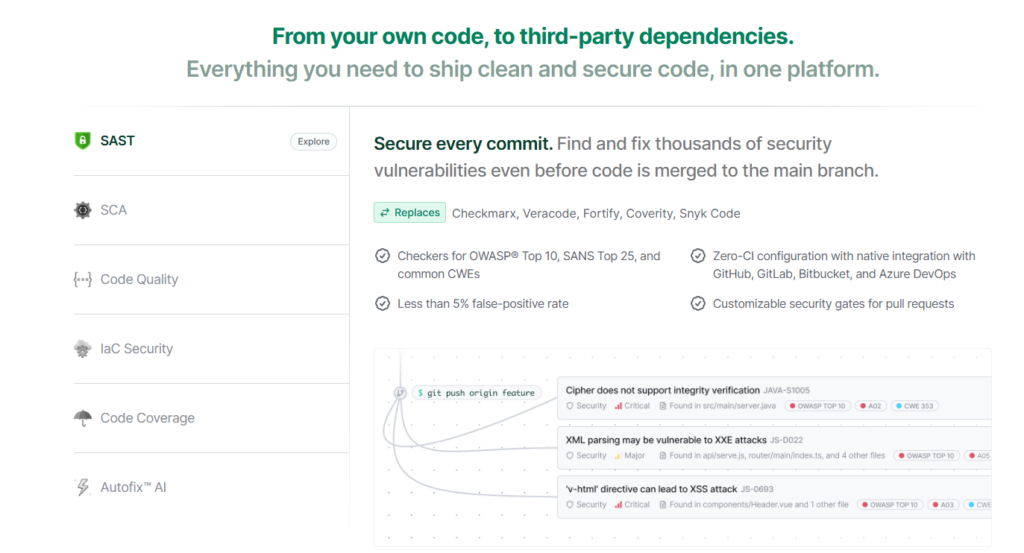
2. Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
DeepSource’s SAST engine goes beyond code quality to find security vulnerabilities:
- Checks against OWASP Top 10 and compliance-relevant weaknesses
- Identifies vulnerabilities such as SQL injection patterns, insecure data handling, and misuses of unsafe APIs
- Prioritizes issues based on severity and impact
Unlike legacy SAST tools that require complex CI integration, DeepSource’s security scanning works out-of-the-box and triggers automatically on every commit.
3. Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
Modern applications embed many open-source dependencies, which can introduce known vulnerabilities. DeepSource includes SCA to:
- Scan dependency manifests
- Report known CVEs and risk vectors
- Provide context-driven risk evaluation
This ensures that your software supply chain doesn’t introduce hidden attack surfaces, aligning with best practices for dependency security.
4. Automated Remediation – Autofix™
One of DeepSource’s defining features is Autofix™, an AI-powered automation engine that:
- Generates suggested fixes for issues detected during analysis
- Can automatically create pull requests with safe remediation code
- Reduces manual effort for developers
Autofix is especially useful for routine issues such as code formatting, simple bug fixes, and common vulnerability patterns — helping teams focus effort on complex logic and architectural decisions rather than repetitive corrections.
5. Workflow Integration and Developer Experience
DeepSource integrates seamlessly with popular version control platforms:
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Bitbucket
- Azure DevOps
Once connected, it automatically runs analysis on pull requests and commits without requiring CI configuration changes. Results — including inline comments — appear directly in the pull request workflow.
Developer-Centric Insights
- Issues surfaced where developers already work
- Prioritized by severity and relevance
- Suppression mechanisms for false positives
- Metric thresholds and quality gates enforce standards before merging
This workflow-first approach reduces context switching, making analysis results more actionable.
6. Reports and Metrics
DeepSource provides detailed reports that help engineering leaders and security teams make sense of project health:
- OWASP Top 10 vulnerability summaries
- CWE/SANS Top 25 risk breakdowns
- Shareable, exportable dashboards
- Trend data and historical analysis
These insights help teams measure progress and demonstrate compliance with internal or regulatory standards.

How DeepSource Works in Practice
1. Repository Activation
Once DeepSource is connected to your version control provider, you:
- Select repositories to analyze
- Configure desired analyzers
- Enable continuous analysis via a
.deepsource.tomlconfig file - Begin receiving automated scans on commits and pull requests
Initial runs establish a baseline of existing issues, while subsequent analysis focuses on new changes.
2. Integration With Development Workflows
DeepSource’s tight integration ensures:
- Results show up inside pull requests
- Blame and remediation context are easy to find
- Quality gates can block merges if thresholds are not met
- Teams can automate code formatting on every commit
This radically reduces the manual effort traditionally associated with code quality enforcement.
3. Customization and Control
Teams can tailor:
- Which analyzers run
- Severity thresholds
- Suppression rules
- Quality gate criteria
This flexibility makes DeepSource suitable for both small teams and enterprise environments, where coding standards may differ significantly.
Comparison With Other Tools
DeepSource is frequently compared to legacy platforms such as SonarQube and enterprise SAST tools like Veracode or Checkmarx. Some key differentiators:
| Capability | DeepSource | SonarQube | Veracode / Checkmarx |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workflow-native pull request analysis | ✔️ | Partial | Limited |
| Automated fixes | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
| No CI configuration | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Developer-focused UX | ✔️ | Mixed | Mixed |
| Transparent pricing | ✔️ | Per LOC pricing | Enterprise pricing |
DeepSource focuses on developer experience and automation, while legacy tools often emphasize broad language support or compliance frameworks — sometimes with more setup overhead.
Limitations and Tradeoffs
While DeepSource delivers strong value, teams should be aware of some limitations:
- Compared with enterprise SAST, comprehensive compliance reporting and deep vulnerability databases may be more limited
- Language coverage, while broad, may not be as extensive as some older tools
- Analysis is scoped to repository context, so cross-repo dependency issues may be harder to detect without supplemental tooling
These gaps can be mitigated by pairing DeepSource with other specialized solutions where necessary.
Conclusion
DeepSource represents a modern take on static code analysis and DevSecOps:
- Automation-first: analyses run without CI configuration
- Developer-first: issues and fixes appear where developers work
- Automation-enabled: Autofix reduces manual remediation effort
- Integrated insights: security, quality, and dependency risks in one pane
By integrating deeply into pull request workflows and providing actionable feedback early in the development process, DeepSource helps teams ship cleaner, more secure code faster — a critical advantage in the age of rapid deployment cycles.
