NVIDIA Alpamayo is a groundbreaking open-source AI platform designed to push autonomous vehicles (AVs) into the era of reasoning-based autonomy — meaning cars that don’t just see the world but can reason about it like a human would. The platform combines large AI models, simulation tools, and extensive real-world datasets into a unified ecosystem aimed at accelerating safe, interpretable Level-4 autonomous driving development.
Traditional autonomous systems largely rely on perception + planning pipelines that treat sensor processing and decision-making as separate, handcrafted modules. These systems typically excel when conditions match their training but struggle in rare, unusual “long tail” scenarios — like an unexpected pedestrian or a blocked lane with ambiguous cues.
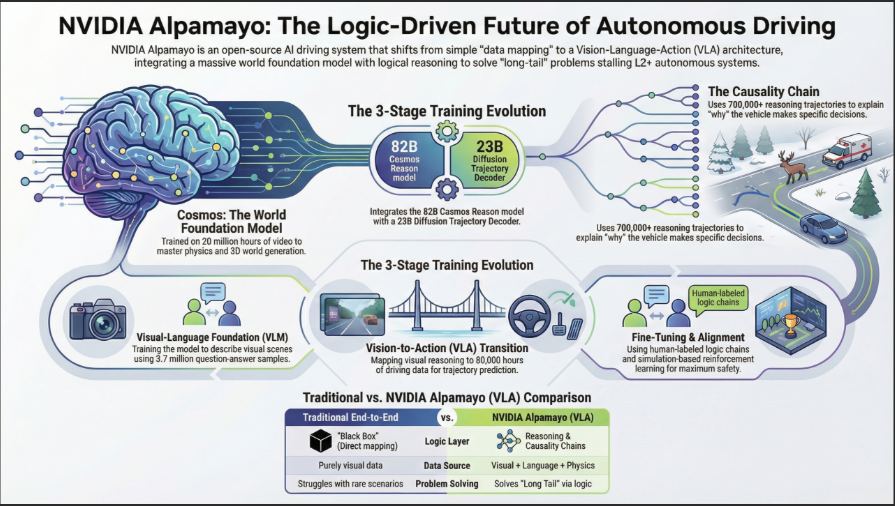
Alpamayo changes this by introducing chain-of-thought reasoning into the heart of autonomy. This means the AI not only predicts trajectories, but produces interpretable reasoning traces that explain why it chose a specific action — catapulting AV software toward safety, explainability, and regulatory compliance.
NVIDIA Alpamayo is a state-of-the-art family of open Vision Language Action (VLA) models that works alongside the open-source AlpaSim simulator and physical AI open datasets. This complete, open toolchain is designed to accelerate the next generation of autonomous vehicles (AVs), using human-like reasoning to handle complex, long-tail driving scenarios more safely and efficiently.
NVIDIA Alpamayo 1 gives you a powerful foundation for building “thinking” autonomous systems by bridging chain-of-thought reasoning with precise trajectory planning. As an open research foundation built on NVIDIA Cosmos™ Reason, you can use this model to:
- Build Interpretability Into Driving: Move beyond “black-box” path planning by generating human-readable reasoning traces that explain why a vehicle makes specific decisions in complex, “long-tail” scenarios.
- Fine-Tune and Distill: Take advantage of the Alpamayo model’s 10B parameters as a teacher to fine-tune and distill into smaller, run-time capable models.
- Evaluate in a High-Fidelity Closed-Loop: Deploy the model directly into the AlpaSim framework and the physical AI open datasets. Benchmark your experimental AV applications against real-world metrics like minADE and AlpaSim scores.
Alpamayo 1 — The Reasoning Vision-Language-Action Model
At the heart of the platform is Alpamayo 1, a 10-billion-parameter Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model designed to handle autonomous driving decisions with human-like reasoning.
Key Technical Attributes:
- Model Size: ~10 billion parameters.
- Architecture: Divided into two functional components:
- ~8.2B-parameter Cosmos-Reason backbone for semantic understanding.
- ~2.3B-parameter Action Expert responsible for translating reasoning into concrete trajectory outputs.
- Input: Multi-modal video + sensor inputs (cameras, lidar, radar).
- Output:
- Planned driving trajectory (e.g., path for next seconds).
- Chain-of-thought reasoning trace describing why the action was chosen.
Unlike traditional black-box neural networks, Alpamayo’s reasoning traces offer transparency — making it possible to audit decisions, improve safety, and support regulatory validation.
Role in Development:
Alpamayo 1 acts as a teacher model. Developers can use it to fine-tune or distill smaller run-time models optimized for in-vehicle deployment, while retaining reasoning capabilities.
AlpaSim — Open-Source Simulation Framework
AlpaSim is a fully open, high-fidelity simulation environment that enables closed-loop testing of autonomous driving policies. It recreates realistic sensor models, vehicle dynamics, traffic behaviors, and environmental conditions — critical for iterating and validating AV systems without real-world risk.
Technical Highlights:
- Modular microservices architecture:
- Services (renderer, physics, traffic sim, driver, controller) run independently and can scale horizontally across GPUs, optimizing throughput and resource usage.
- Pipeline parallelism: Enables overlapping rendering and inference tasks to increase simulation efficiency.
- Closed-loop feedback: AI decisions influence future sensor states and simulated world responses — a more realistic test of a driving policy’s robustness than static data replay.
This simulator closes the gap between model training and deployment by offering a platform where perception, reasoning, and control are evaluated together.
Physical AI Open Datasets
NVIDIA is releasing a massive open dataset — one of the most diverse available for autonomous driving research — with 1,700+ hours of driving data captured across many geographies and complex conditions.
Dataset Characteristics:
- Multi-sensor capture: Synchronized high-resolution cameras, lidar, and radar.
- Global coverage: Data from 25+ countries and thousands of cities.
- Edge cases included: Rare, safety-critical events (e.g., unusual traffic patterns, erratic pedestrian behavior).
This dataset fuels training of VLA models and supports benchmarking across diverse scenarios — essential to avoid overfitting to narrow conditions.
Integration with NVIDIA’s Autonomous Ecosystem
While Alpamayo is open source, it integrates naturally with NVIDIA’s broader automotive technology stack, including DRIVE OS and DRIVE hardware accelerators (e.g., DRIVE AGX Thor). Hardware that supports high-throughput AI inference is critical to running large reasoning models in real-time with low latency.
Other integrations possible for ‘A2Z’ and ‘RideFlux’
This alignment ensures developers can use Alpamayo tools from training and simulation straight through to in-vehicle deployment.
Autonomous Driving Capability Matrix
| Capability / Feature | NVIDIA Alpamayo | Autonomous A2Z | RideFlux |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Solution | Open AI research & development platform | Full-stack autonomous vehicle technology and deployment | Full-stack autonomous driving software + services |
| Primary Focus | AV development foundation, reasoning & simulation tools | Vehicle deployment and commercial autonomous services | Urban Level 4 autonomous driving operation and commercialization |
| Target Use Cases | R&D, simulation, training, explainable autonomy | Public shuttles, smart city mobility, logistics, deployments | Robotaxi services, public transport, freight and logistics trials |
| Commercial Deployment | Not a vehicle product — supports developers & OEMs | Yes — operates autonomous vehicles and services | Yes — operates autonomous services (buses, unmanned operations) |
| Openness & Licensing | Fully open models, tools, datasets | Proprietary technology | Proprietary technology |
| Core Offering | Foundational AI models, simulation, datasets | Full autonomy stack + hardware + vehicles | Full autonomy stack software + operations |
| Reasoning & Decision AI | Vision-Language-Action (VLA) chain-of-thought models for reasoning & explanations; alpamayo1 ~10B | Uses proprietary perception and planning systems | Uses proprietary perception and planning systems |
| Simulation Support | AlpaSim: open high-fidelity closed-loop simulator | Uses internal or third-party simulation for validation | Uses internal or third-party simulation for development |
| Datasets | Physical AI Open Datasets: ~1,700+ hours diverse driving data | Uses its own collected real-world data | Uses its own collected real-world data |
| Perception Stack | Model-agnostic (vision+sensor inputs for reasoning) | In-house sensor processing (e.g., cameras, LiDAR, radar) | In-house sensor processing (perception, prediction, planning, control) |
| Localization / Mapping | Support through datasets and models for training | Full localization & vector/HD map integration | Full localization (GNSS/IMU + maps) |
| Prediction / Planning | Reasoning & “chain of thought” model that can support planning logic | Proprietary planning stack for real vehicles | Proprietary planning stack for real vehicles |
| Control Algorithms | Can be used to train control policies via simulation | On-vehicle control algorithms included / redundancy systems | Integrated control stack in software |
| Safety & Redundancy | Provides core models; safety implementation left to developer | Redundant architecture, safety controllers, remote emergency control | Operational safety engineering for public deployment |
| Operational Design Domain (ODD) | Research-focused, broad scenarios | Urban, smart city, industrial zones | Urban roads, freeway + urban contexts |
| Regulatory Certification Aid | Interpretability and audit capability from reasoning models | Works towards Level-4 certification for vehicles | Conducts permit-based unmanned tests and commercialization |
| Commercial Service Experience | No direct service operations | Yes — shuttles, public transit, pilot operations | Yes — public transport and robotaxi services |
| Partnership & Ecosystem Role | Foundation tools used by OEMs / research | Autonomous vehicle developer and deploying partner | Autonomous vehicle developer + service operator |
| Key Strength | Open ecosystem for building AV intelligence | End-to-end AV deployment & hardware/software integration | Urban mobility services with deployed Level-4 autonomous vehicles |
Alpamayo for Autonomous Vehicle Development | NVIDIA Developer
