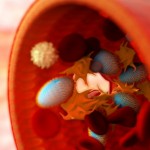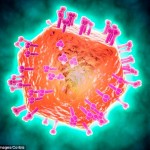
HIV breakthrough could lead to a cure

Borrow and enjoy audiobooks, eBooks, comics, movies, TV, magazines, or music everywhere you have a screen-your computer, your phone, your car, even your TV. All you need is a library card. hoopla syncs across all your devices, so you can stream titl...
Read More
LibreOfficeLibreOffice is mostly known for being an open-source replacement for Microsoft Office. Beyond the standard editing of documents (Writer), spreadsheets (Calc), and presentations (Impress), it also has tools for databases (Base), calculations (Math)....
Read More
Salvatore Oriti, mechanical engineer in the Thermal Energy Conversion Branch at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, adjusts the Stirling testbed in preparation for testing at the center in January 2025. Credit: NASA/Jef Janis To exp...
Read More
Mathematicians Uncover a New Class of Digitally Delicate Primes Prime numbers — integers greater than 1 that are divisible only by 1 and themselves — are among the most foundational and mysterious objects in mathematics. From Euclid’s proof of their infini...
Read More